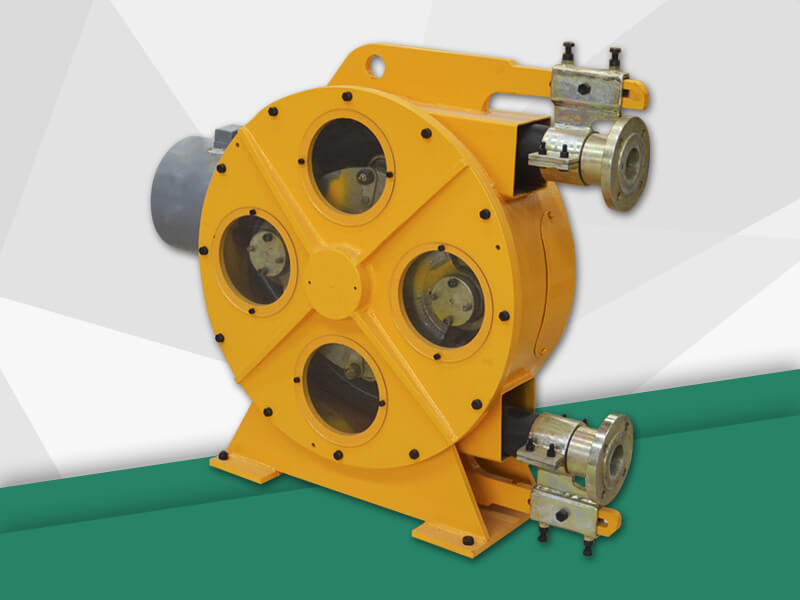
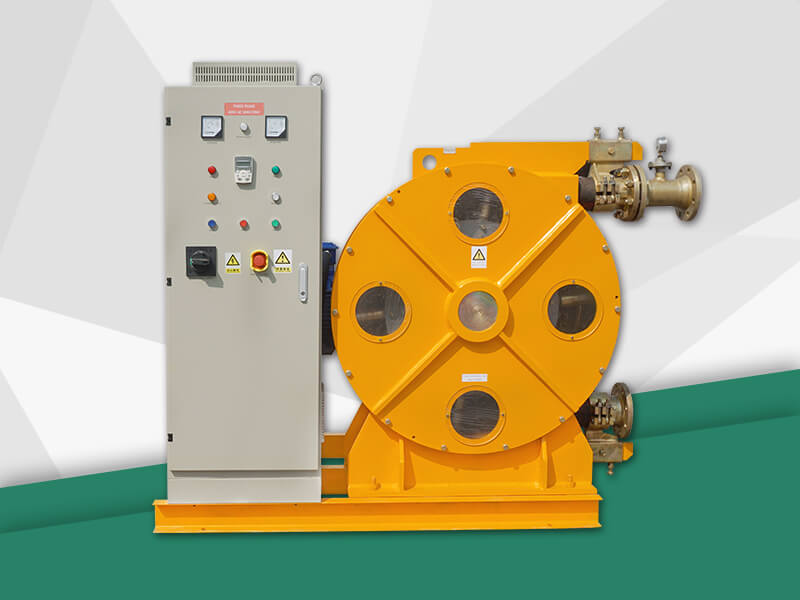
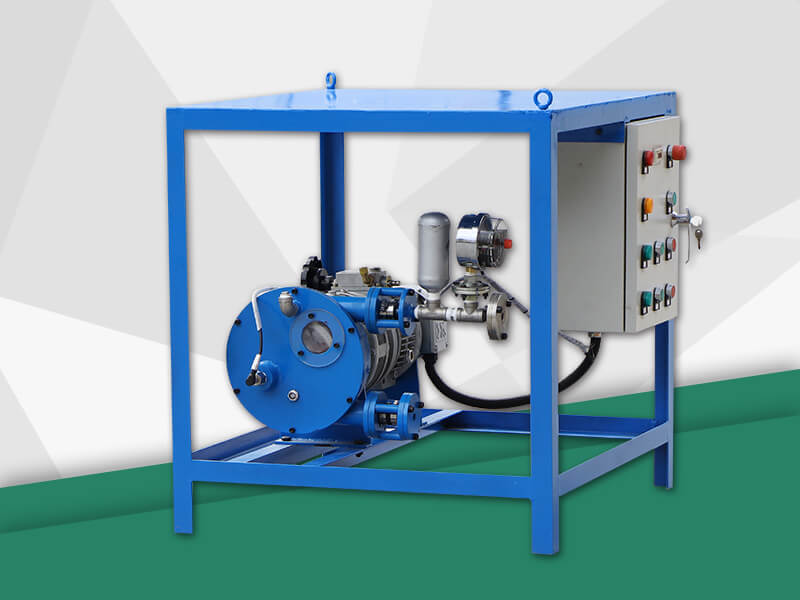
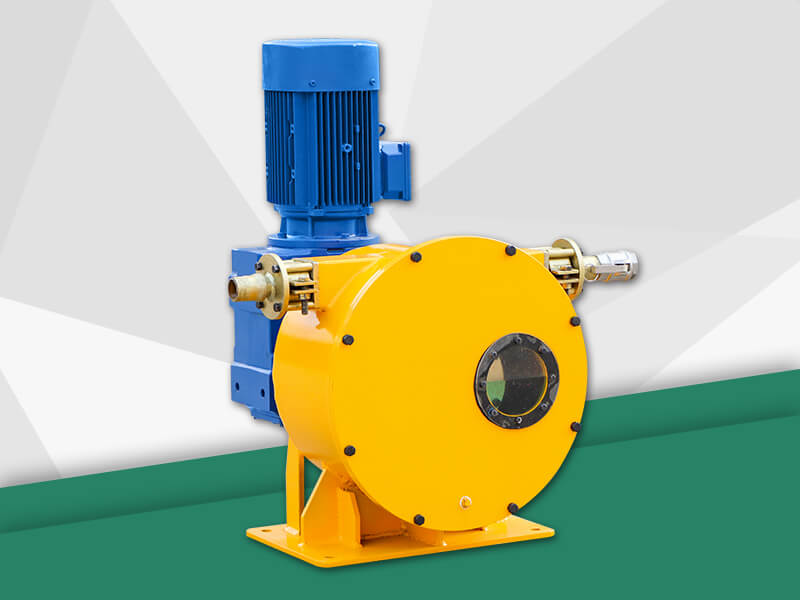
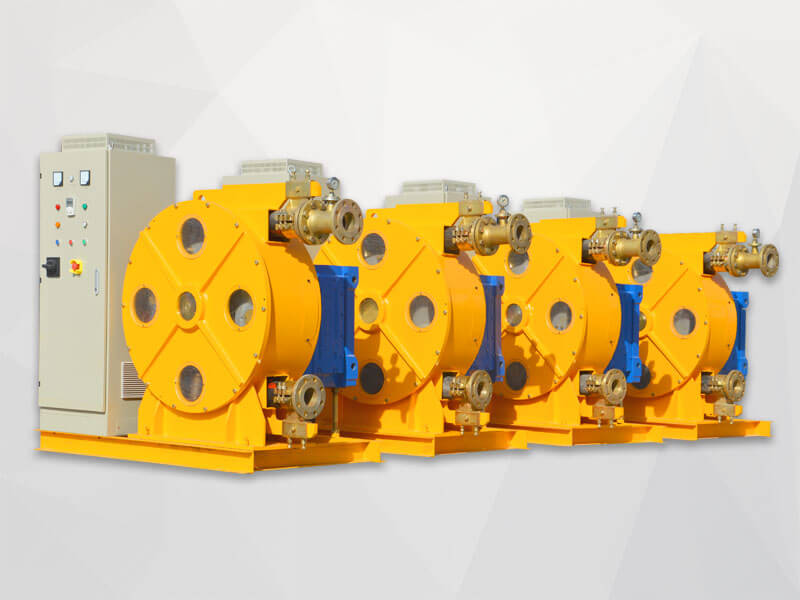
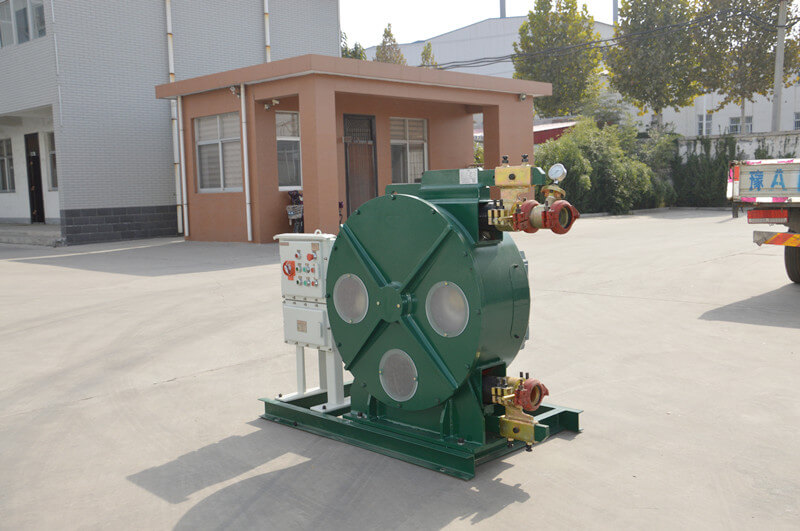
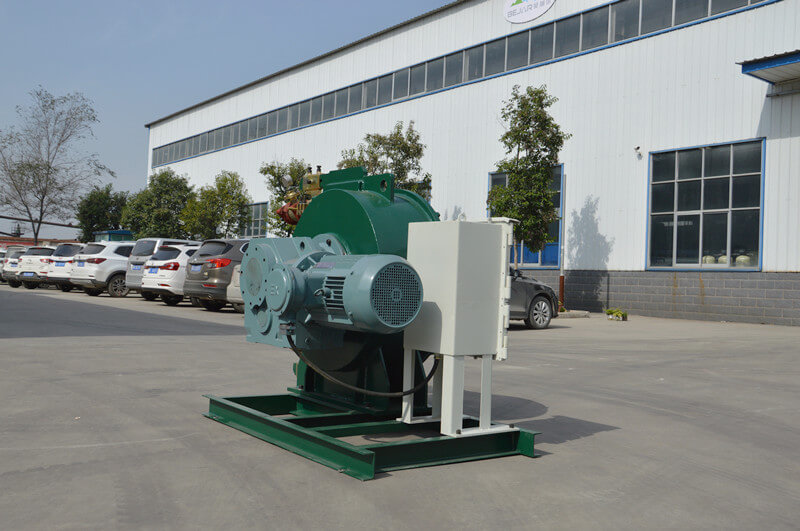
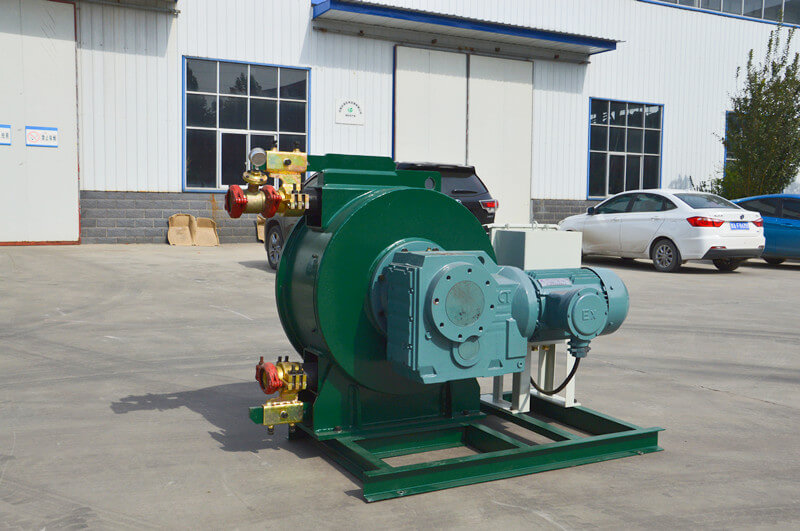
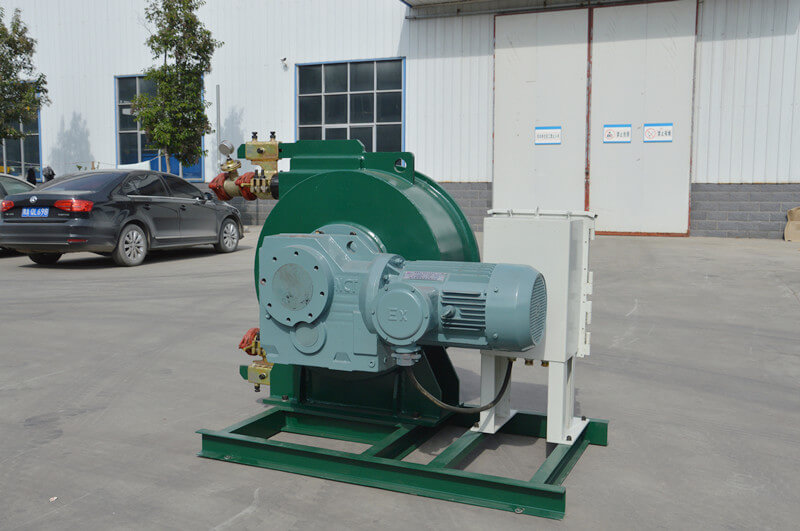
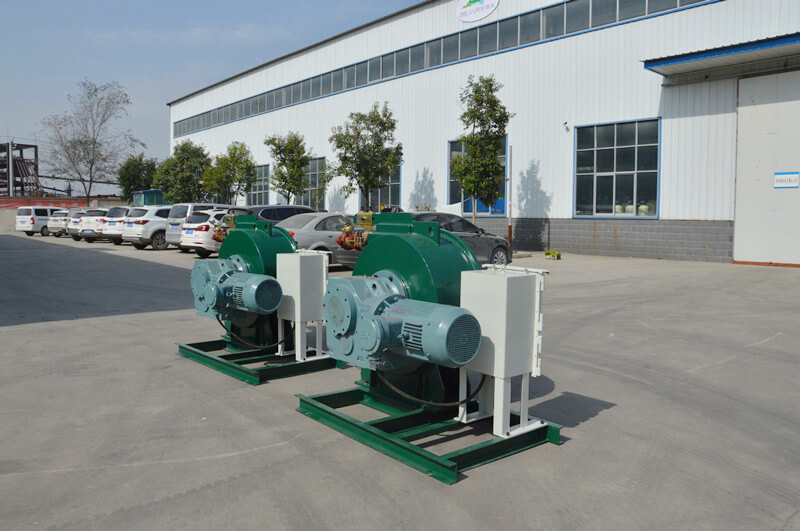
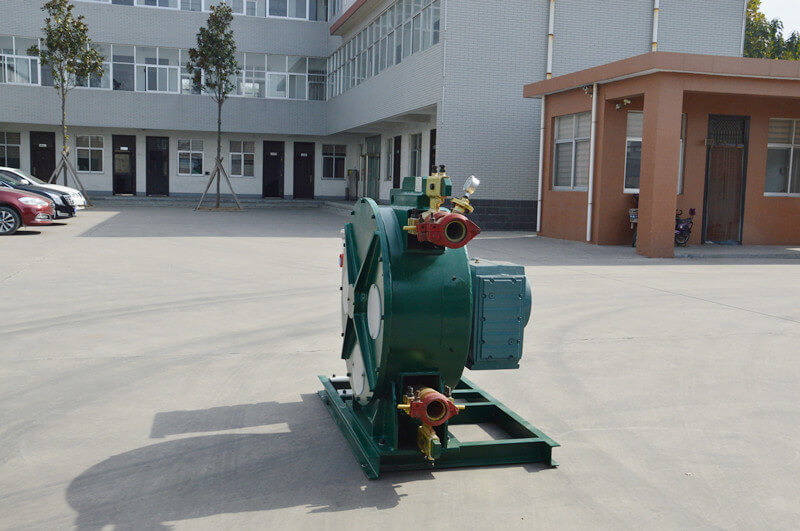
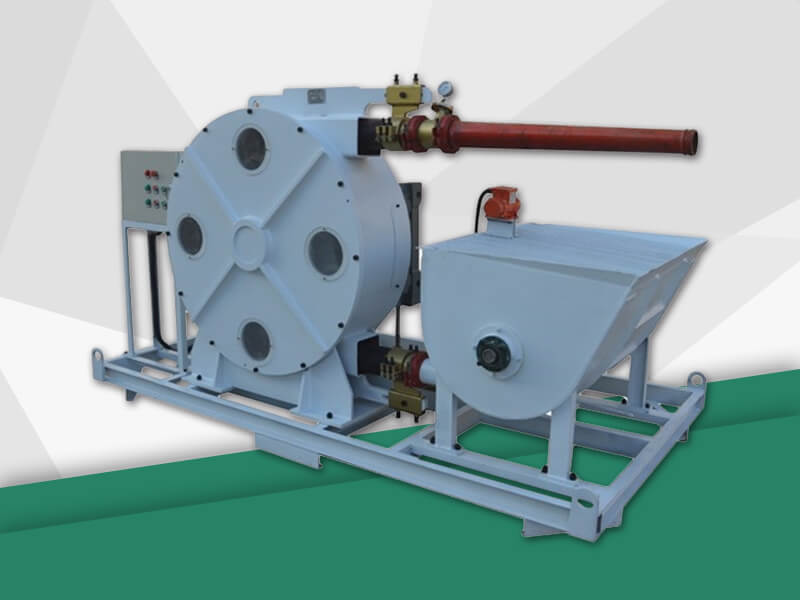
Peristaltic wastewater tubing pump designers and users are primarily interested in the ability to transport highly abrasive media. There are no valves or seals. Only the internal cavity of the hose comes into contact with the medium. The rotor of the compression hose is completely independent of the medium. In addition, hose pumps have many unique features. No other pump has better self-priming capacity than a hose pump and can create an almost complete vacuum to absorb liquids. Transports gas-containing liquids and foamed liquids without gas resistance.
Peristaltic wastewater tubing pump for sale can transport highly viscous, shear-sensitive media. The fixed displacement and outlet pressure are not related to the natural metering pump, respectively. Due to various advantages, soft KP tube pumps are increasingly widely used in industries such as gold smelting, non-ferrous metal smelting, chemical industry, mining, food processing, brewing, ceramics and water treatment.
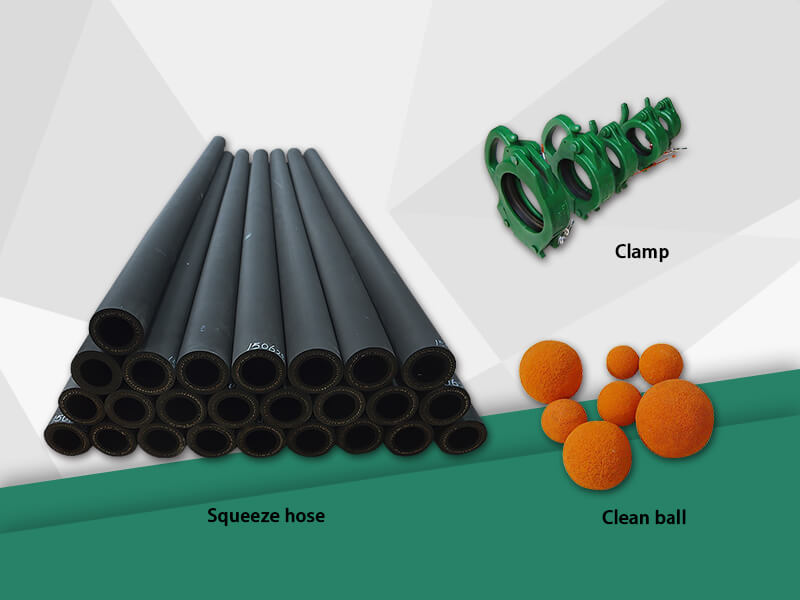
The life of a high quality peristaltic wastewater tubing pump is 7-10 years. The biggest challenge is the hose pump hose. This is the core of the hose pump. Its life is directly related to the cost of the pump. Hose pumps are designed to maximize hose life. Some people intuitively believe that the abrasiveness of the medium determines the life of the hose, but this is a misunderstanding.
Abrasive media cause wear on the inner wall of the hose, thinning the known thickness of the inner wall of the hose, causing internal leaks or backflow, resulting in reduced flow rates due to loose compression. Internal drainage further increases wear.. However, high quality hose pumps require a hose compression regulator. This device is constantly tuned during use of the pump to prevent flow and flow drop.
Regardless of the compatibility of the transport medium and hose material, the peristaltic wastewater tubing pump hose has the same service life when transporting strong abrasive media and non-abrasive mucus. In fact, in addition to the type and manufacturing quality of the hose itself, the number of compressed hoses is a major factor in determining the life of the hose. The second factor is the method and force of the compression hose and the resulting frictional heat. .. In other words, hose failure is due to accumulated compression time and fatigue aging due to frictional heat.
The best way to maximize hose life and extend downtime intervals is to use compression methods that minimize the number of compression hoses and minimize hose damage and accurate compressive strength.