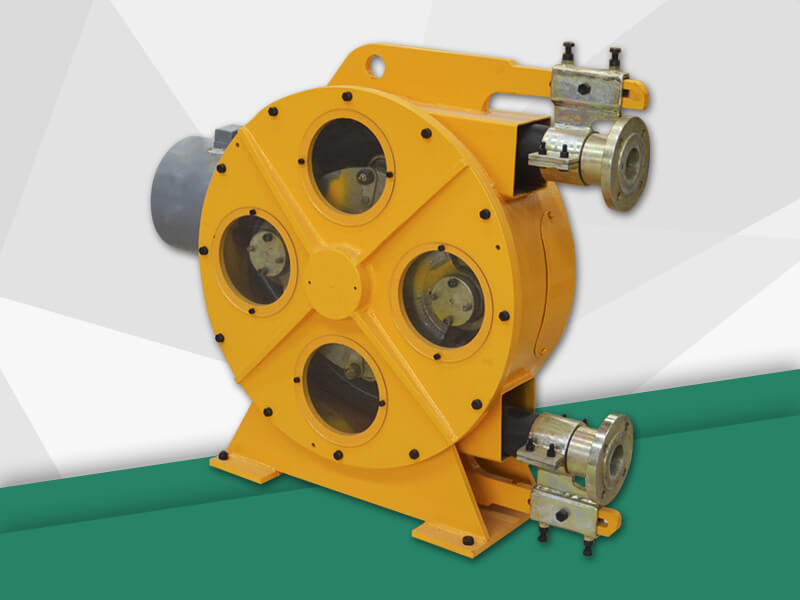
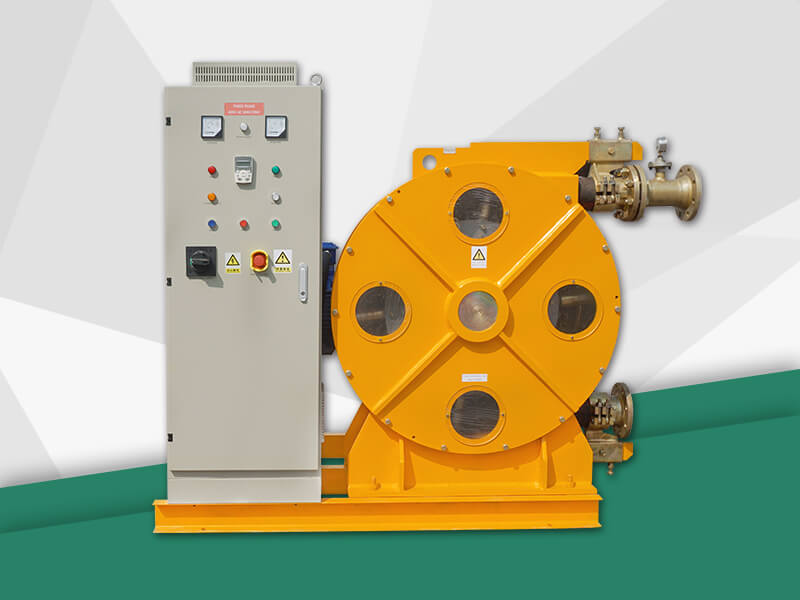
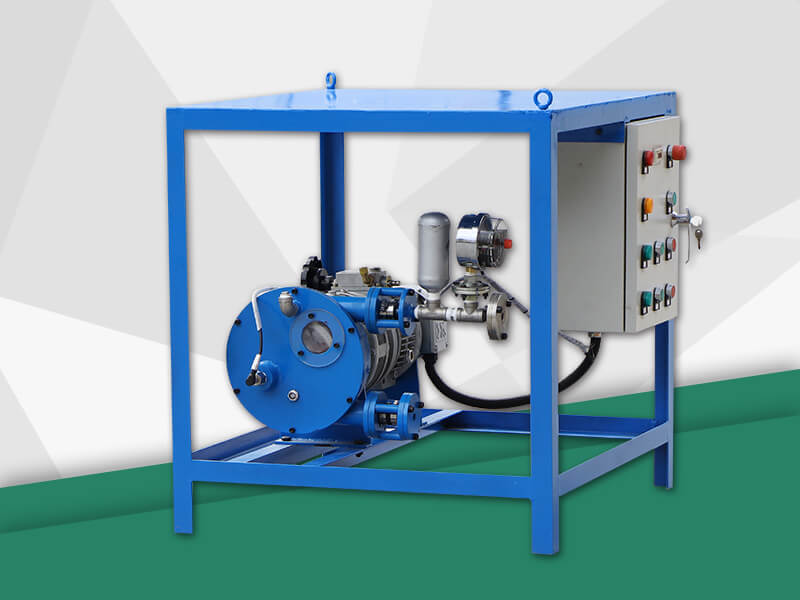
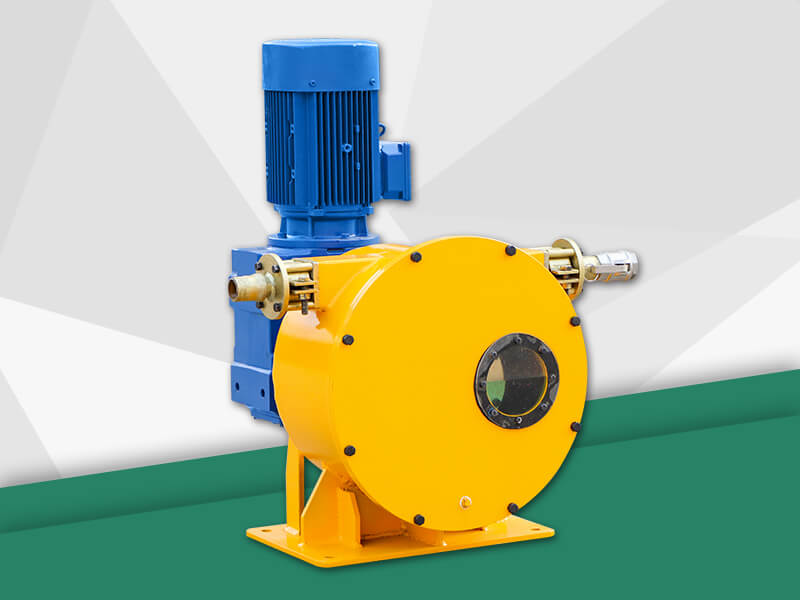
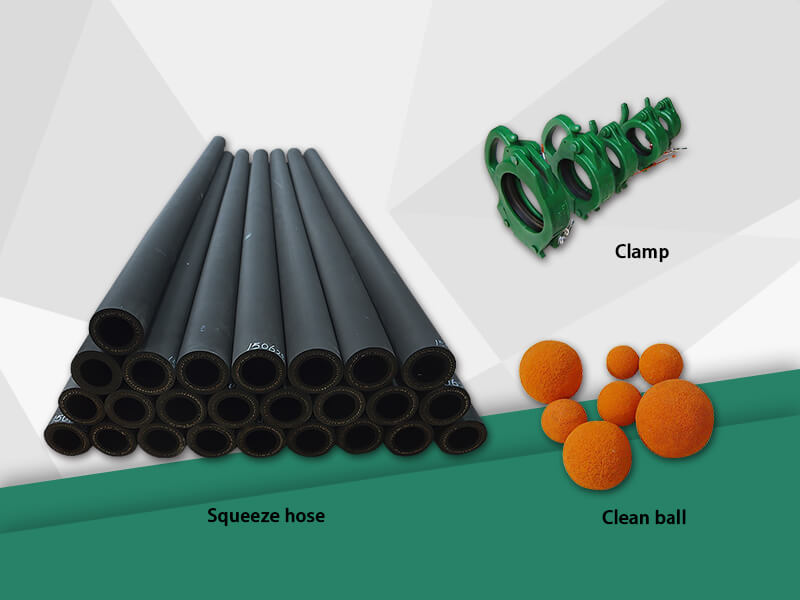
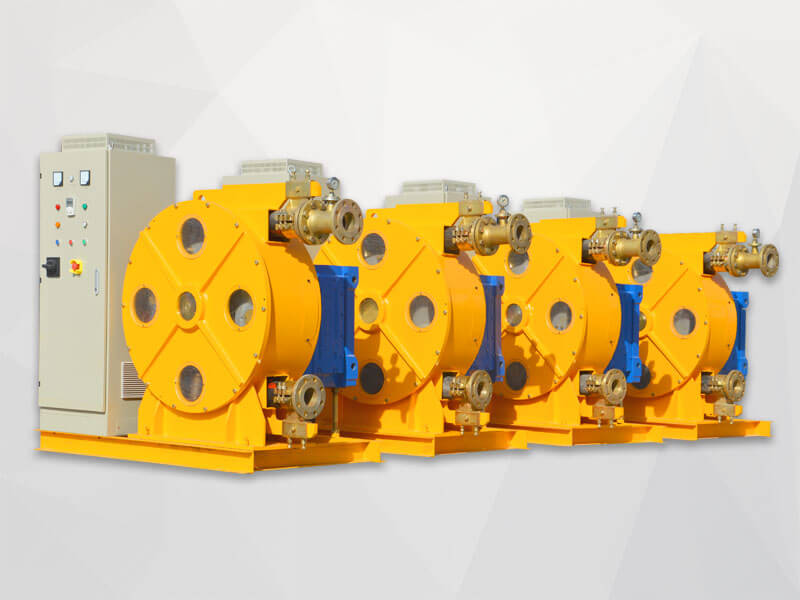
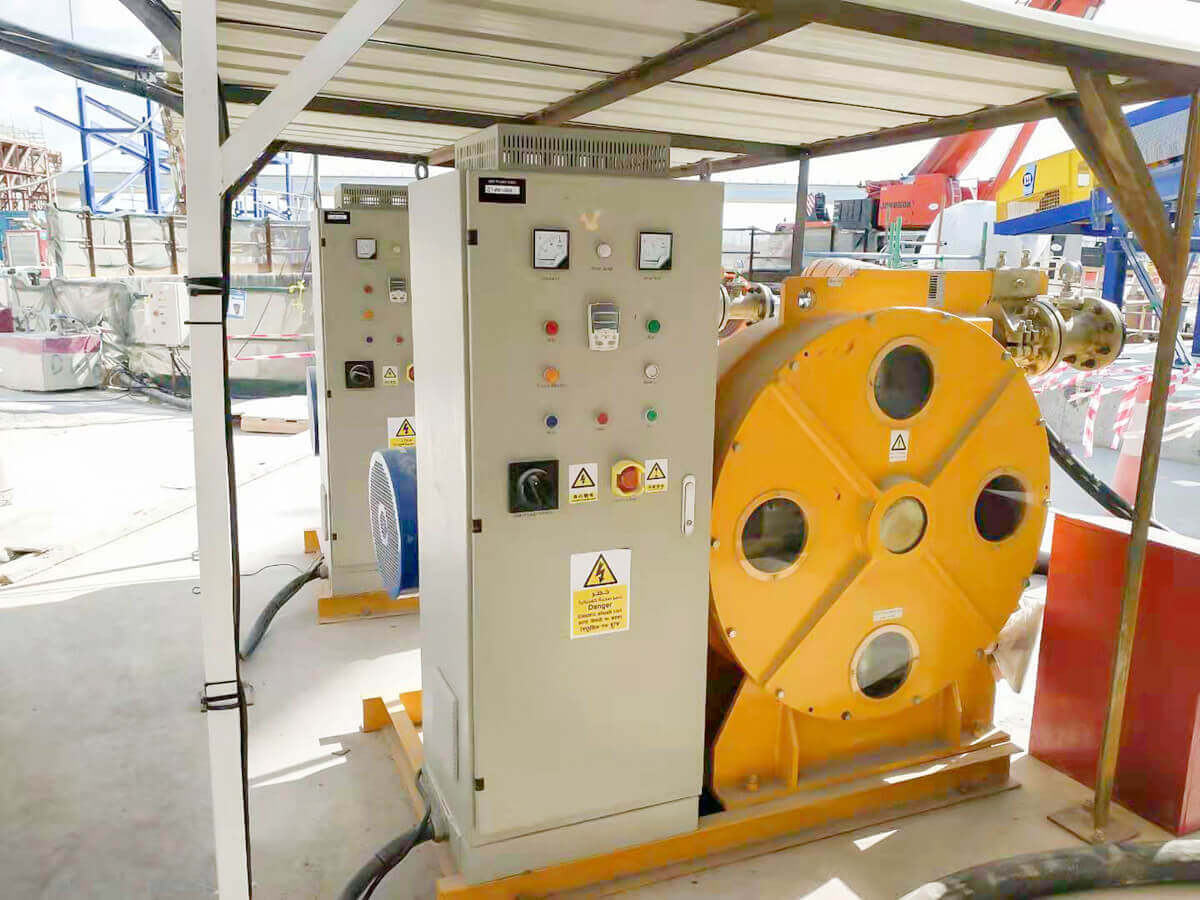
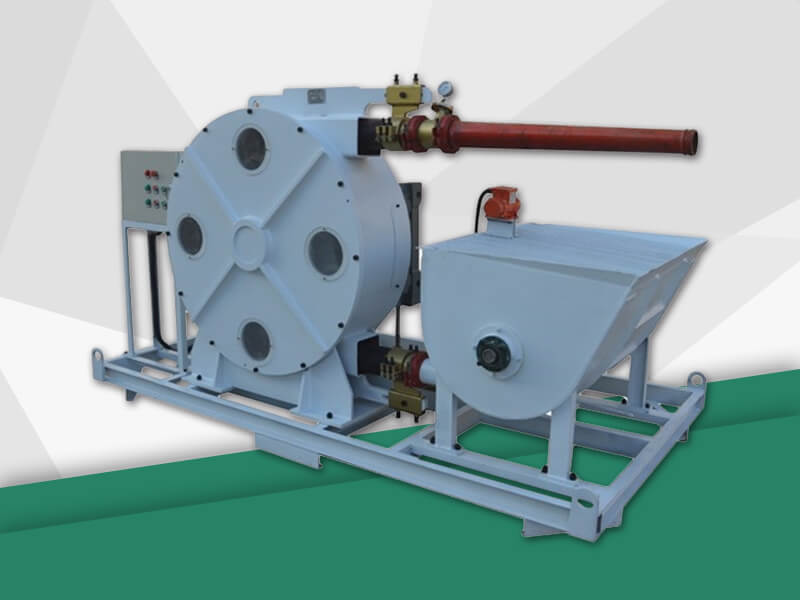
The hose pump is composed of a hose, a roller mounted on the rotor, and the pump casing. When the rotor is rotated, the inner cavity of the hose formed by the roller and the pump casing squeezes gradually from the formation, and this cavity is gradually increased. Liquid is being sucked. When the rotor is turned to squeeze the hose, the liquid that has entered the cavity is squeezed loose by the roller to the closed cavity. When the rotor continues to roll, this part of the liquid is squeezed to communicate with the pump outlet. The continuous rotation of the rotor will form a continuous "creep" of the hose, which will continuously transport liquid from the low pressure inlet of the pump to the high pressure outlet. Various advantages make the hose pump more and more widely used Chemical, mining, food processing, brewing, ceramics, water treatment and other industries.
Hose pumps confine chemical media in the pipeline so that the pump cannot come into contact with the fluid and the fluid cannot come into contact with the pump. This pollution-free pumping makes hose pumps particularly suitable for high-purity applications, including the transfer or metering of chemicals and additives in food, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor applications. Squeeze hose pumps are suitable for dispensing, metering and general conveying applications. Generally, the peristaltic tube pump's flow rate is as low as 0.01 to 50 m3 / h, and it can generate a pressure of up to 3Mpa (Trelleborg hose). It has high strength abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance. Performs well with toxic chemical media.
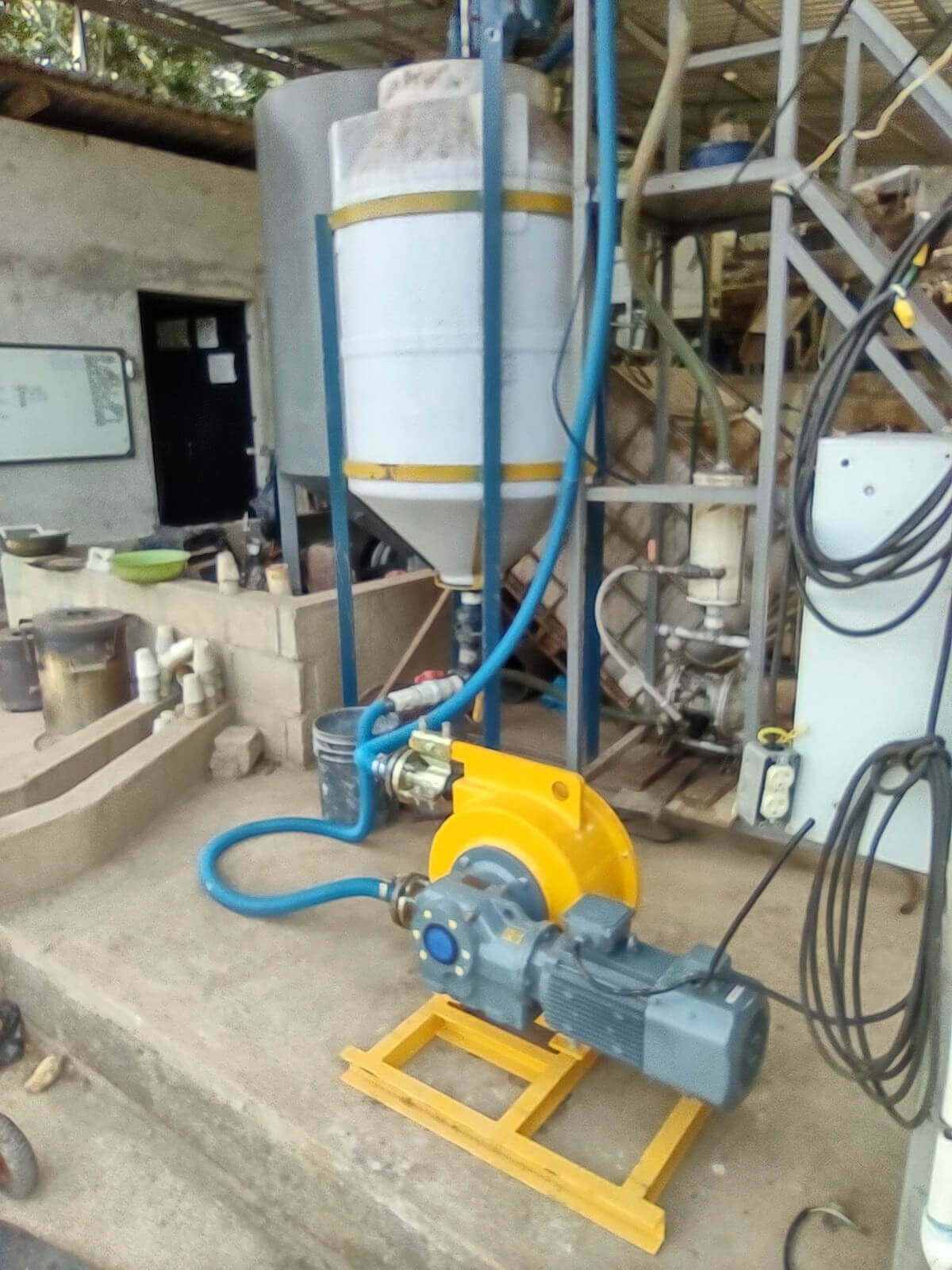
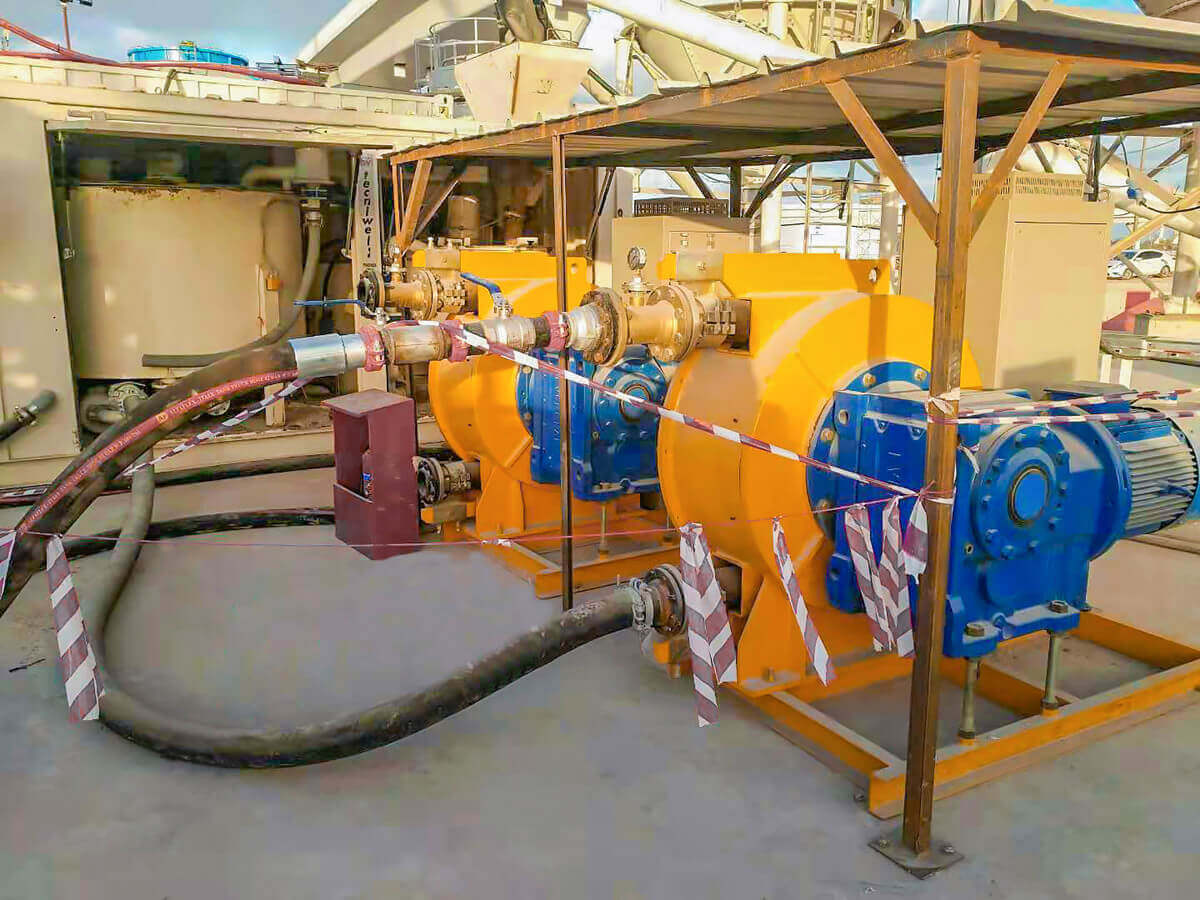
In addition, because chemical media is limited to the pipeline, hose pumps are easier to maintain and reduce downtime compared to other pump technologies. The hose pump uses a flexible tube through a roller in the pump head. As fluid flows through the pump head, a packet of fluid is formed. The flow depends on the size of the package and the rotation speed of the drum. By controlling the size of the pipe and the speed of the pump head, accurate metering of the medium can be achieved. Hose pumps are ideal for use in laboratory, pilot plant and process applications, offering a variety of configurations, from low cost fixed speed pumps to advanced controlled models for critical metering and distribution applications.
The hose pump has a simple structure and is relatively easy to manufacture. The life and durability of the pump mainly depend on the elasticity and corrosion resistance of the pipe. Its flow rate is related to the speed of the motor and the inner diameter of the tube. So the key is to choose a pipe and a speed control mechanism. As long as the pipe has a long life and a stable speed, there is no problem in maintaining the quantitative transportation for a long time.
When dealing with the fluid of a hose pump, the hose should show a certain good chemical performance, which is called chemical compatibility. Such as: low adsorption, good temperature resistance, not easy to aging, non-swelling, corrosion resistance, low precipitates, etc., chemical resistance decreases with increasing temperature, and chemicals that do not affect the tube at room temperature may change with temperature Elevation affects the hose.